strep pneumoniae test on blood agar put drops of|streptococcus pneumoniae hemolysis : discount store Blood agar can be made selective for certain pathogens by the addition of antibiotics, chemicals or dyes. Examples includes crystal violet blood agar to select Streptococcus pyogens from throat swabs, and kanamycin or . webOnline Roulette Guide im Jahr 2024: Finden Sie hier die besten Roulette Casinos online. Roulette Varianten, Echtgeld Gewinne, kostenlose Spiele und Boni!
{plog:ftitle_list}
Follow Mia Khalifa (@miakhalifa) on Twitter to get the latest updates on her life, opinions, and projects. See what she tweets, likes, and replies to other users. Join the .
1. Isolation on Blood agar. Pneumococci frequently require enriched media and increased CO 2 tension for initial isolation. They are usually isolated on Blood agar and incubated in a candle jar (a closed container in which a lit candle is . Blood agar can be made selective for certain pathogens by the addition of antibiotics, chemicals or dyes. Examples includes crystal violet blood agar to select Streptococcus pyogens from throat swabs, and kanamycin or .
bubbles and froth on the surface. (NOTE: Cooling the agar and warming the blood are essential steps in this proced ure. Hot agar can damage red blood cells, and cold blood can cause the agar to gel before pouring.) PROTOCOL Interpretation* of Hemolysis on Blood Agar Plates (*) To read the hemolytic reaction on a blood agar plate, the plate must Despite vaccination programs, Streptococcus pneumoniae remains among the main microorganisms involved in bacterial pneumonia, notably in terms of severity. The prognosis of pneumococcal infections is . Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States, and the cost of these hospitalizations is estimated to cost up to billion in the United States (US) dollars each year. Thirty-day hospital mortality associated with CAP has been estimated to be as high as 22% and is the leading cause of death amongst all infectious .
Bile Solubility Test is a biochemical experiment used to distinguish Streptococcus pneumoniae from other alpha-hemolytic streptococci. . streak the test organism onto a blood agar plate. Application of Bile Salt: Apply a few drops of the 2% sodium deoxycholate solution straight to a well-isolated colony on the blood agar plate. Incubation: Bile Solubility Test is the test which differentiate Streptococcus pneumoniae (positive- soluble) from alpha-hemolytic streptococci (negative- insoluble).Streptococcus pneumoniae is bile soluble whereas all other alpha-hemolytic streptococci are bile resistant.. Principle of Bile Solubility Test. S. pneumoniae has an autolytic enzyme which can be .FOR ALPHA OR GAMMA HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCUS: OPTOCHIN SENSITIVITY TEST. This test differentiates Streptococcus pneumoniae from other alpha hemolytic streptococci. S. pneumoniae is sensitive to the chemical optochin (ethylhdrocupreine hydrochloride) and will be inhibited from growing around the optochin disk. 1. Label half of a blood agar plate .
Principle. Bacitracin test is used to determine the effect of a small amount of bacitracin (0.04 IU or 0.05 IU not higher) on an organism. Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococci) is inhibited by the small amount of bacitracin in the disk; other beta-hemolytic streptococci usually are not. Some laboratories do not recommend the use of 0.04 U bacitracin disk as Lancefield groups C . Information on group A strep bacteria and the health problems they can cause. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. . are gram-positive cocci that grow in chains. They exhibit β-hemolysis (complete hemolysis) when grown on blood agar plates. They belong to group A in the Lancefield classification system for β-hemolytic . Biochemical Test and Identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae. They are gram +ve, catalase -ve, oxidase -ve, non-sporing, diplococci bacteria. . 2 thoughts on “Biochemical Test and Identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae” . AM Tiny colony with LLF type on CLED, Small whites slightly mucoid colony in carrom coins colony on chocolate .
Rapid and early identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae from positive blood cultures is crucial for the management of patients with bloodstream infections (BSI). Many identification systems in microbiology laboratories have difficulty differentiating S. pneumoniae from other closely related species in the Streptococcus mitis group. To overcome this .
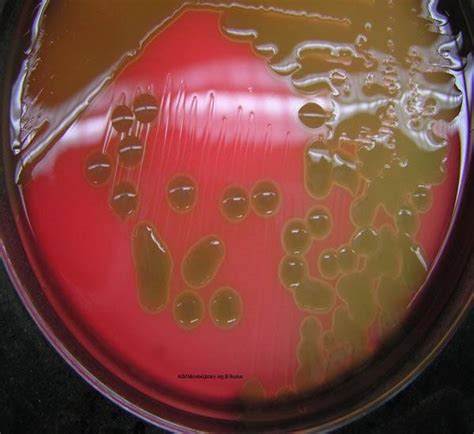
streptococcus pneumoniae on blood agar
Streptococcus pneumoniae or Strep. pneumoniae can be broken down into strepto- which means chain, -coccus, which means round shape, and pneumoniae, which refers to the fact that it causes pneumonia - no surprises there.. So, Strep pneumoniae are round bacteria that tend to grow in chains, usually in lancet-looking pairs called diplococci. They’re the most common .Agar is the solidifying agent. Sheep blood is added to enhance the growth of Streptococcus pneumoniae. with a white background and contrasting black lines. In the disk diffusion test, disks impregnated with a specific concentration of antibiotic are placed on the surface of an inoculated Mueller Hinton Agar plate.Pneumococcal disease can affect many different systems in your body. It may result in conditions with mild symptoms like a sinus infection (sinusitis).But it can also lead to pneumonia, blood infection (sepsis) or bacterial meningitis — and may be life-threatening at any age.. Treatment typically involves antibiotics.Vaccines can reduce the risk of infection, especially in young .Pneumococcal Media Todd Hewitt. Todd Hewitt broth with yeast extract is a popular liquid media used for the cultivation of S. pneumoniae.Its inception stems from studies by Todd and Hewitt on the metabolic functions of the pneumococcus (Todd and Hewitt, 1932).The earlier version of this broth constituted of a meat broth with added 2% proteose peptone (enzymatic digest of .
Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC® 6305 Positive Streptococcus sanguis ATCC® 10556 Negative LIMITATIONS 1. When using the spot test, read a positive test as colony disintegration and not a floating-away of the colony on the surface of the reagent.10 2. Use bile solubility only to differentiate alpha-hemolytic streptococci from S. pneumoniae.10 3.Streptococcus pneumoniae on Blood Agar . Note the mucoid, transluscent colonies and the alpha hemolysis (partial hemolysis typically accompanied by a greenish discolorization of the agar around and under the growth). .
Morphology. To identify S. pyogenes in clinical samples, blood agar plates are screened for the presence of β-hemolytic colonies. The typical appearance of S. pyogenes colonies after 24 hours of incubation at 35-37°C is dome-shaped with a smooth or moist surface and clear margins. They display a white-greyish color and have a diameter of > 0.5 mm, and .
The AccuProbe Streptococcus pneumoniae culture identification test (Gen-Probe, San Diego, CA) was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions using well-isolated 18- to 24-h colonies from 5% sheep blood agar. The combining of the DNA probe with target organism rRNA to form a labeled DNA-RNA hybrid was indicated by a luminometer .MICROBIOLOGY DIAGNOSIS: Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria are gram-positive cocci arranged in chains and pairs (diplococci) on microscopic examination. A green, α-hemolytic, zone surrounds S. pneumoniae colonies on blood-agar plates. Pneumococci can be differentiated from other catalase-negative viridans streptococci by their susceptibility to Optochin and .inoculated to ensure recovery of microorganisms that may be inhibited on selective agar. 2. Inoculate Strep Selective Agar by rolling the swab over a small area of the agar surface. Use a sterile inoculating loop to streak for isolation. Stab the agar several times with the loop in the area of heaviest inoculation.Streptococcus mitis ATCC 49456- negative (bile insoluble). Procedure Plate Spot Test. Place one drop of 10% bile solubility reagent near suspected 18- to 24-hour-old colonies growing on sheep blood agar. Gently roll the drop over several representative colonies by tilting the plate. Take care not to dislodge the colonies.
Streptococcus pneumoniae Growing on Blood Agar (Indirect Lighting) Note the mucoid colonies, alpha hemolysis (greenish discolorization of the red blood cells around the colonies) and sensitivity to the drug optochin in the Taxo P® disc. Photograph from From MicrobeLibrary.org Alpha. When alpha hemolysis (α-hemolysis) is present, the agar under the colony is dark and greenish. Streptococcus pneumoniae and a group of oral streptococci (Streptococcus viridans or viridans streptococci) display alpha hemolysis.This is sometimes called green hemolysis because of the color change in the agar. Alpha hemolysis is caused by .Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococci) are gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic, aerobic, encapsulated diplococci. Pneumococcal infection is a major cause of otitis media, pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis, and death. . Alpha-hemolysis on blood agar. Sensitivity to optochin. Lysis by bile salts. . The urine antigen detection test has high specificity .Abstract. Streptococcus pneumoniae is both an aggressive pathogen and a normal part of the human respiratory microbiome. Clinicians and microbiologists have struggled to develop tests that can identify pneumococcal respiratory infection and accurately distinguish colonization from invasive disease.
Positive: Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619, Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 6305. Negative: Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212, Streptococcus sanguis ATCC 15506. Limitations. Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates should be incubated in a CO 2 enriched environment, as some isolates will grow poorly or not at all.
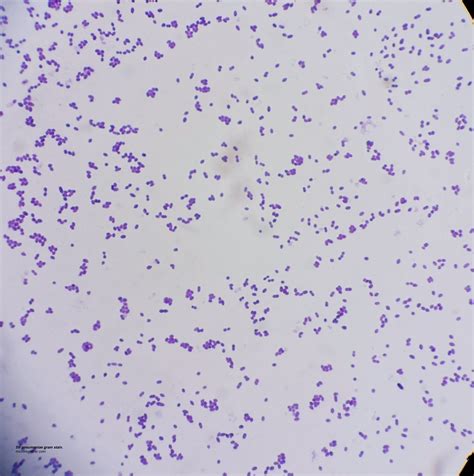
streptococcus pneumoniae microscopic image
Resultado da 17 de abr. de 2023 · Musa do OnlyFans, Stephanie Silveira afirma ter recebido uma proposta generosa de um sheik de Dubai. A modelo diz que .
strep pneumoniae test on blood agar put drops of|streptococcus pneumoniae hemolysis